
What is a Heat Pump and Why You'll Love It
What Are Heat Pumps?
Did you know that, even on the coldest days of the year when you’re shivering outside, you’re still surrounded by heat?
Electric heat pumps extract heat energy from cold air to provide warmth for your home. Although they work best in mild climates, they can be used in conjunction with other units to heat homes in even the coldest places. With a heat pump, you'll enjoy energy savings and unmatched comfort.
What Does a Heat Pump Look Like?
 A heat pump looks virtually identical to an air conditioning system. It has an outdoor unit that contains a coil and compressor, as well as an indoor air handler. The two are connected by a refrigerant line.
A heat pump looks virtually identical to an air conditioning system. It has an outdoor unit that contains a coil and compressor, as well as an indoor air handler. The two are connected by a refrigerant line.
This makes sense when you realize that a heat pump is an air conditioner in reverse. In fact, heat pumps can change to air conditioners during the warm months. Let’s take a closer look at heat pump operation and the parts of a heat pump.
How Does a Heat Pump Work?
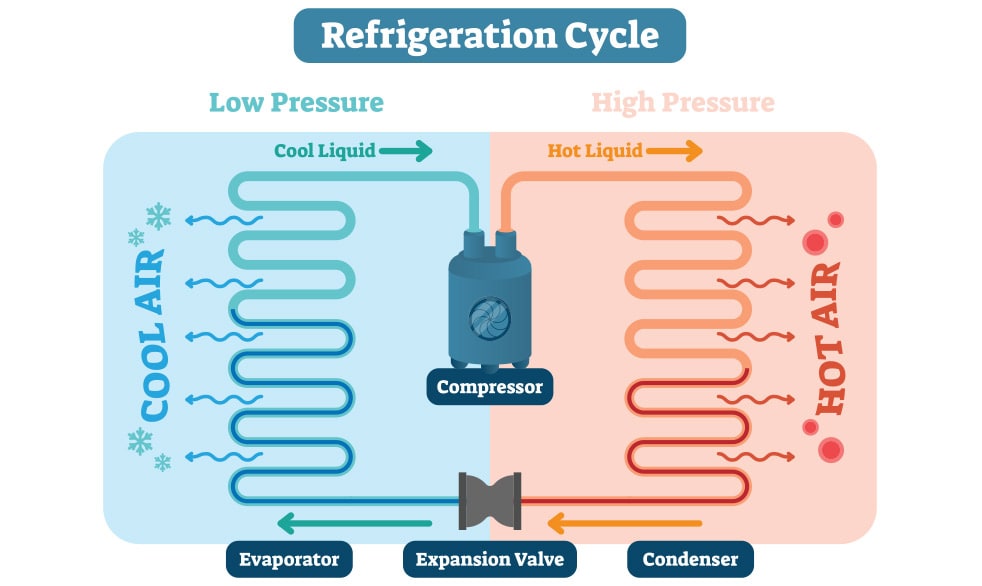
At the most basic level, a heat pump absorbs heat from outdoor air and brings it inside your house. It operates on the principle that heat is naturally drawn to cold. The key is the refrigerant that transports heat between the indoor and outdoor coil.
- Cold refrigerant flows through the outdoor coil and picks up warmth from the outdoor air (even though it’s cold outside, it’s still warmer than the refrigerant, so heat transfer occurs).
- The warmed refrigerant flows into a compressor, which compresses it and makes it hot (compressing a substance makes it hotter).
- The heated refrigerant now flows into the indoor coil. Cold air from your home blows over the refrigerant and absorbs the heat, which is then distributed throughout your home via air ducts.
- The refrigerant is now cooler, but still not cold enough to repeat the cycle. Next, it flows through an expansion valve and becomes cold (expanding a substance makes it colder).
- Finally, the cold refrigerant flows back to the outdoor coil to repeat the process.
If you want a familiar example of how a heat pump works, think of your refrigerator, which operates on the same principles. Cold refrigerant picks up heat from inside the refrigerator and moves it outside.
That’s why the back and sides of your fridge are warm to the touch—the heat is being dissipated into your kitchen from inside the fridge.
Air Conditioning Mode
During the summer, there is a reversing valve on the heat pump that you can flip. This reverses the flow of refrigerant and turns the heat pump into an air conditioner.
In air conditioning mode, the cold refrigerant picks up heat from your house and dumps it outside. Learn more about how an air conditioner works.
Types of Heat Pumps
There are two main types of heat pumps:
- Central heat pumps provide heat for your entire house from one, central location. They use an air handler to circulate the warm air throughout your home’s ductwork. Learn more about air handlers.
- Ductless heat pumps, also known as mini splits, heat individual rooms and can be combined to heat your whole house. They let you enjoy different temperatures in different rooms. Learn more about mini splits.
How Efficient is a Heat Pump?
 Heat pumps are highly efficient because they don’t need to use much energy to heat your home. Unlike a gas furnace that must create its own heat with a burner, a heat pump simply transfers heat from outside to inside.
Heat pumps are highly efficient because they don’t need to use much energy to heat your home. Unlike a gas furnace that must create its own heat with a burner, a heat pump simply transfers heat from outside to inside.
It’s like the difference between baking a pie from scratch at home versus transporting one from the store. You spend much more time and effort making the pie versus just moving it from point A to point B.
Heat pump efficiency is expressed by one of two ratings:
- Seasonal energy efficiency rating (SEER)-used to rate A/C units.
- Heating seasonal performance factor (HSPF)-used to rate heating units.
The higher those ratings, the more efficient your heat pump will be.
High efficiency doesn’t necessarily mean your heat pump will be less expensive to run than a gas furnace, however. That depends on the cost of electricity versus gas in your area, which you should research before buying a unit. Since they run on electricity, heat pumps are most affordable in areas where electrical costs are low.
At What Temperature Does a Heat Pump Stop Working?
 Many buyers wonder about this when they first hear about heat pumps. It’s true that if you consistently see temperatures fall well below freezing, a heat pump alone may not be an efficient way to heat your home.
Many buyers wonder about this when they first hear about heat pumps. It’s true that if you consistently see temperatures fall well below freezing, a heat pump alone may not be an efficient way to heat your home.
Central heat pumps begin losing effectiveness around 40 degrees Fahrenheit, but mini split heat pumps offer an array of products that heat all the way down to -13 degrees Fahrenheit, albeit less efficiently at that point.
In the north, you can still get a central heat pump and use it as an air conditioner during the summer and as a heater during the milder temperatures of spring and autumn. During winter, we recommend other systems such as gas furnaces, radiant heaters and baseboard heaters. Learn more about heaters.
Stay Warm
In short, a heat pump is an energy efficient alternative to heating your home that will squeeze the last drop of warmth from outdoor air.
Unless you have extremely high electricity costs in your area, you can benefit from the savings and comfort provided by a heat pump. If you have questions about how it might work in your home, please contact us at (866) 631-6389.





